Develop an AI Agent with Azure AI Agent Service
In this exercise you’ll use Azure AI Agent Service to create a simple agent that analyzes data and creates charts. The agent uses the built-in Code Interpreter tool to dynamically generate the code required to create charts as images, and then saves the resulting chart images.
This exercise should take approximately 30 minutes to complete.
Create an Azure AI Foundry project
Let’s start by creating an Azure AI Foundry project.
-
In a web browser, open the Azure AI Foundry portal at
https://ai.azure.comand sign in using your Azure credentials. Close any tips or quick start panes that are opened the first time you sign in, and if necessary use the Azure AI Foundry logo at the top left to navigate to the home page, which looks similar to the following image:
- In the home page, select + Create project.
- In the Create a project wizard, enter a suitable project name for (for example,
my-ai-project) and if an existing hub is suggested, choose the option to create a new one. Then review the Azure resources that will be automatically created to support your hub and project. - Select Customize and specify the following settings for your hub:
- Hub name: A unique name - for example
my-ai-hub - Subscription: Your Azure subscription
- Resource group: Create a new resource group with a unique name (for example,
my-ai-resources), or select an existing one - Location: Select Help me choose and then select gpt-4 in the Location helper window and use the recommended region*
- Connect Azure AI Services or Azure OpenAI: Create a new AI Services resource with an appropriate name (for example,
my-ai-services) or use an existing one - Connect Azure AI Search: Skip connecting
* Model quotas are constrained at the tenant level by regional quotas. In the event of a quota limit being reached later in the exercise, there’s a possibility you may need to create another project in a different region.
- Hub name: A unique name - for example
- Select Next and review your configuration. Then select Create and wait for the process to complete.
-
When your project is created, close any tips that are displayed and review the project page in Azure AI Foundry portal, which should look similar to the following image:
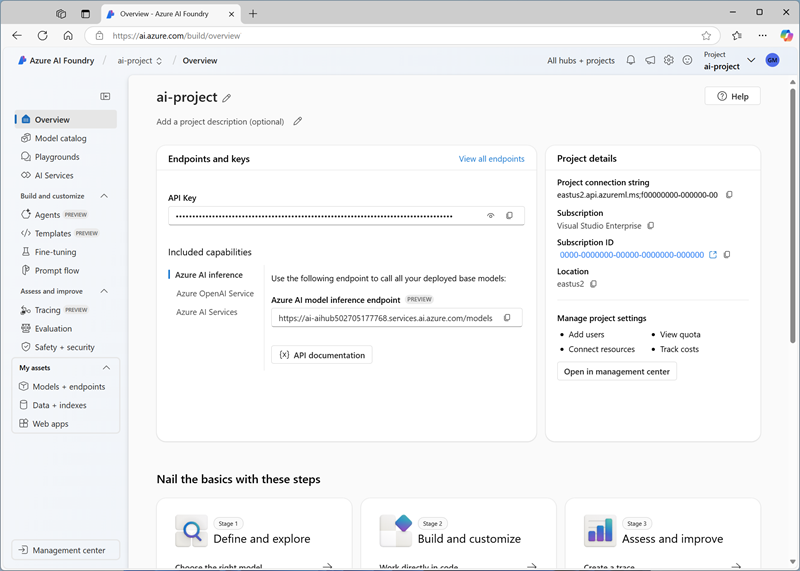
- In the project overview page, in the Project details area, note the Project connection string. Later, you’ll use this connection string to connect to your project in a client application.
Deploy a generative AI model
Now you’re ready to deploy a generative AI language model to support your agent.
- In the pane on the left for your project, in the My assets section, select the Models + endpoints page.
- In the Models + endpoints page, in the Model deployments tab, in the + Deploy model menu, select Deploy base model.
- Search for the gpt-4 model in the list, and then select and confirm it.
- Deploy the model with the following settings by selecting Customize in the deployment details:
- Deployment name: A unique name for your model deployment - for example
gpt-4-model(remember the name you choose - you’ll need it later) - Deployment type: Standard
- Model version: Select the default version
- Connected AI resource: Select your Azure OpenAI resource connection
- Tokens per Minute Rate Limit (thousands): 5K
- Content filter: DefaultV2
- Enable dynamic quota: Disabled
Note: Reducing the TPM helps avoid over-using the quota available in the subscription you are using. 5,000 TPM is sufficient for the data used in this exercise.
- Deployment name: A unique name for your model deployment - for example
- Wait for the deployment provisioning state to be Completed.
Create an agent client app
Now you’re ready to create a client app that uses an agent. Some code has been provided for you in a GitHub repository.
Clone the repo containing the starter code
- Open a new browser tab (keeping the Azure AI Foundry portal open in the existing tab). Then in the new tab, browse to the Azure portal at
https://portal.azure.com; signing in with your Azure credentials if prompted. -
Use the [>_] button to the right of the search bar at the top of the page to create a new Cloud Shell in the Azure portal, selecting a PowerShell environment. The cloud shell provides a command line interface in a pane at the bottom of the Azure portal.
Note: If you have previously created a cloud shell that uses a Bash environment, switch it to PowerShell.
-
In the cloud shell toolbar, in the Settings menu, select Go to Classic version (this is required to use the code editor).
Ensure you've switched to the classic version of the cloud shell before continuing.
-
In the PowerShell pane, enter the following commands to clone the GitHub repo containing the code files for this exercise:
rm -r ai-agents -f git clone https://github.com/graememalcolm/ai-agents ai-agentsTip: As you enter commands into the cloudshell, the ouput may take up a large amount of the screen buffer and the cursor on the current line may be obscured. You can clear the screen by entering the
clscommand to make it easier to focus on each task. -
Enter the following command to change the working directory to the folder containing the code files and list them all.
cd ai-agents/labfiles/agent-app/python ls -a -lThe provided files include application code and a file for configuration settings.
Configure the application settings
-
In the cloud shell command line pane, enter the following command to install the libraries you’ll use:
pip install python-dotenv azure-identity azure-ai-projects -
Enter the following command to edit the configuration file that has been provided:
code .envThe file is opened in a code editor.
- In the code file, replace the your_project_connection_string placeholder with the connection string for your project (copied from the project Overview page in the Azure AI Foundry portal), and the your_model_deployment placeholder with the name you assigned to your gpt-4 model deployment.
- After you’ve replaced the placeholders, use the CTRL+S command to save your changes and then use the CTRL+Q command to close the code editor while keeping the cloud shell command line open.
Write code for an agent app
Tip: As you add code, be sure to maintain the correct indentation.
-
Enter the following command to edit the code file that has been provided:
code agent.py - Review the existing code, which retrieves the application configuration settings, loads data from data.txt to be analyzed, and creates an AIProjectClient for your Azure AI Foundry project.
-
Under the comment Define an agent that uses the CodeInterpreter tool, add the following code to complete the app:
# Define an agent that uses the Code Interpreter tool with project_client: code_interpreter = CodeInterpreterTool() agent = project_client.agents.create_agent( model=MODEL_DEPLOYMENT, name="data-agent", instructions="You are an AI agent that analyzes data. If the user requests a chart, you create it and save it as a .png file.", tools=code_interpreter.definitions, tool_resources=code_interpreter.resources, ) print(f"Using agent: {agent.name}") # Loop until the user types 'quit' while True: # Get input text user_prompt = input("Enter a prompt (or type 'quit' to exit): ") if user_prompt.lower() == "quit": break if len(user_prompt) == 0: print("Please enter a prompt.") continue # Create and run a thread with a user prompt message # (the prompt includes the data from the file) thread = project_client.agents.create_thread() message = project_client.agents.create_message( thread_id=thread.id, role="user", content=f"{user_prompt} - {data}", ) run = project_client.agents.create_and_process_run(thread_id=thread.id, agent_id=agent.id) # Check the run status for failures if run.status == "failed": print(f"Run failed: {run.last_error}") # Get messages from the thread and print the last one from the agent messages = project_client.agents.list_messages(thread_id=thread.id) last_msg = messages.get_last_text_message_by_role("assistant") if last_msg: print(f"Last Message: {last_msg.text.value}") # Get any files from the messages and save them to the app folder for file_path_annotation in messages.file_path_annotations: project_client.agents.save_file(file_id=file_path_annotation.file_path.file_id, file_name=Path(file_path_annotation.text).name) print(f"File saved as {Path(file_path_annotation.text).name}") # Delete the agent when done project_client.agents.delete_agent(agent.id) - Review the code, using the comments to understand how it:
- Creates a new agent that uses the built-in code interpreter tool and which has explicit instructions.
- Runs a thread with a prompt message from the user along with the data to be analyzed.
- Checks the status of the run in case there’s a failure
- Retrieves the messages from the completed thread and displays the last one sent by the agent.
- Saves each file that was generated.
- Deletes the agent when it is no longer required.
- Save the code file (CTRL+S) when you have finished. You can also close the code editor (CTRL+Q); though you may want to keep it open in case you need to make any edits to the code you added. In either case, keep the cloud shell command line pane open.
Sign into Azure and run the app
-
In the cloud shell command line pane, enter the following command to sign into Azure.
az loginYou must sign into Azure - even though the cloud shell session is already authenticated.
- When prompted, follow the instructions to open the sign-in page in a new tab and enter the authentication code provided and your Azure credentials. Then complete the sign in process in the command line, selecting the subscription containing your Azure AI Foundry hub if prompted.
-
After you have signed in, enter the following command to run the application:
python agent.pyThe application runs using the credentials for your authenticated Azure session to connect to your project and create and run the agent.
-
When prompted, view the data that the app has loaded from the data.txt text file. Then enter a prompt such as:
What's the highest value category?Tip: If the app fails because the rate limit is exceeded. Wait a few seconds and try the prompt again.
-
View the response. Then enter another prompt, this time requesting a chart:
Create a pie chart by category. -
The agent should selectively use the code interpreter tool as required, in this case to create a chart based on your request.
-
Enter
quitto end the application. -
When the application has finished, use the download command to download each .png file that was saved in the app folder. For example:
download ./<file_name>.pngThe download command creates a popup link at the bottom right of your browser, which you can click to download and open the file.
Summary
In this exercise, you used the Azure AI Agent Service SDK to create a client application that uses an AI agent. The agent uses the built-in Code Interpreter tool to run dynamic code that creates images.
Clean up
If you’ve finished exploring Azure AI Agent Service, you should delete the resources you have created in this exercise to avoid incurring unnecessary Azure costs.
- Return to the browser tab containing the Azure portal (or re-open the Azure portal at
https://portal.azure.comin a new browser tab) and view the contents of the resource group where you deployed the resources used in this exercise. - On the toolbar, select Delete resource group.
- Enter the resource group name and confirm that you want to delete it.